Alpine climate: balance sheet summer half-year 2024
Twice a year, the German Weather Service, MeteoSwiss and GeoSphere Austria publish a joint evaluation of the current climate in the Alpine region and how it fits into the long-term trend. The report for the summer half-year 2024 (May to October) has just been published (see link below).
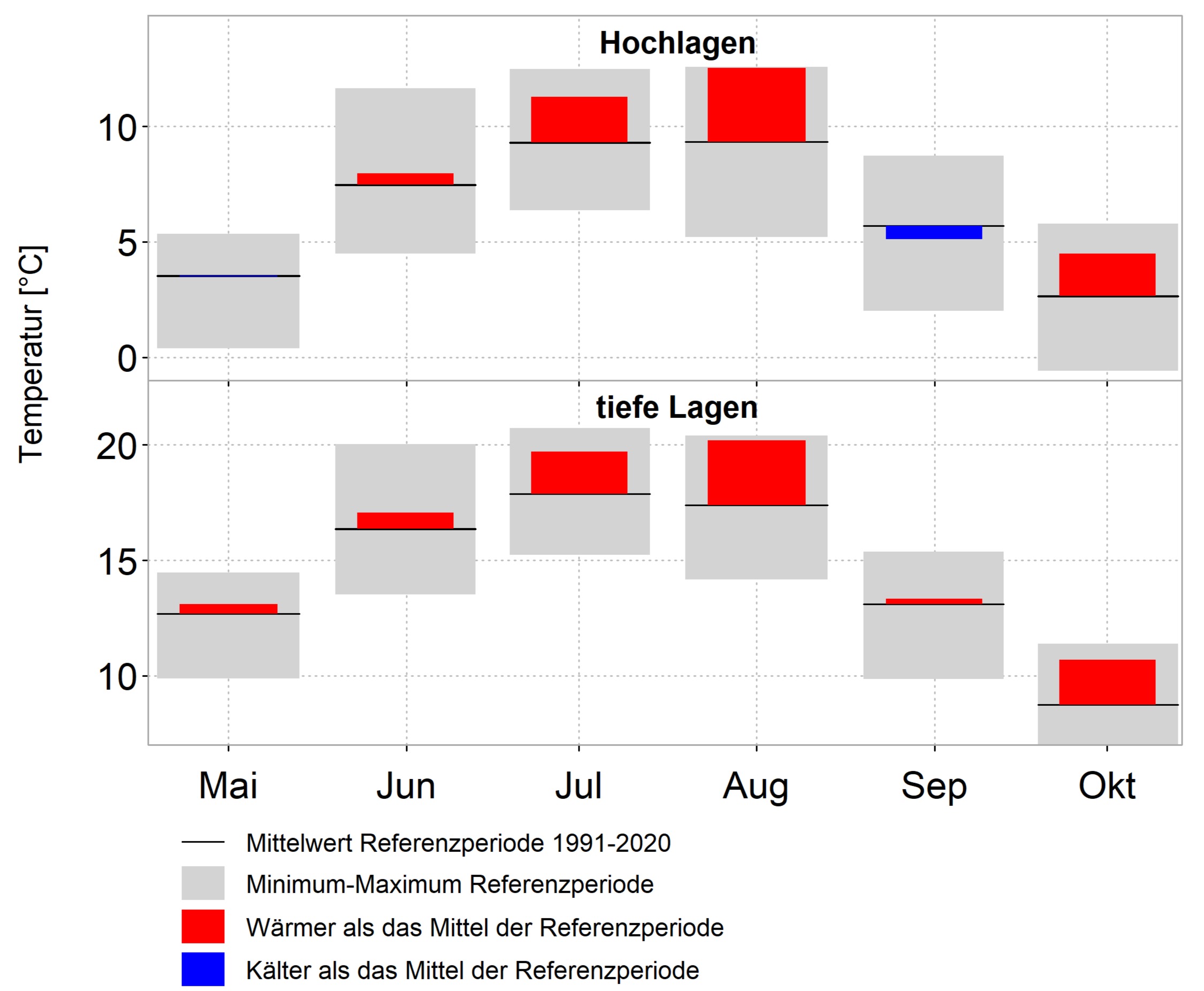
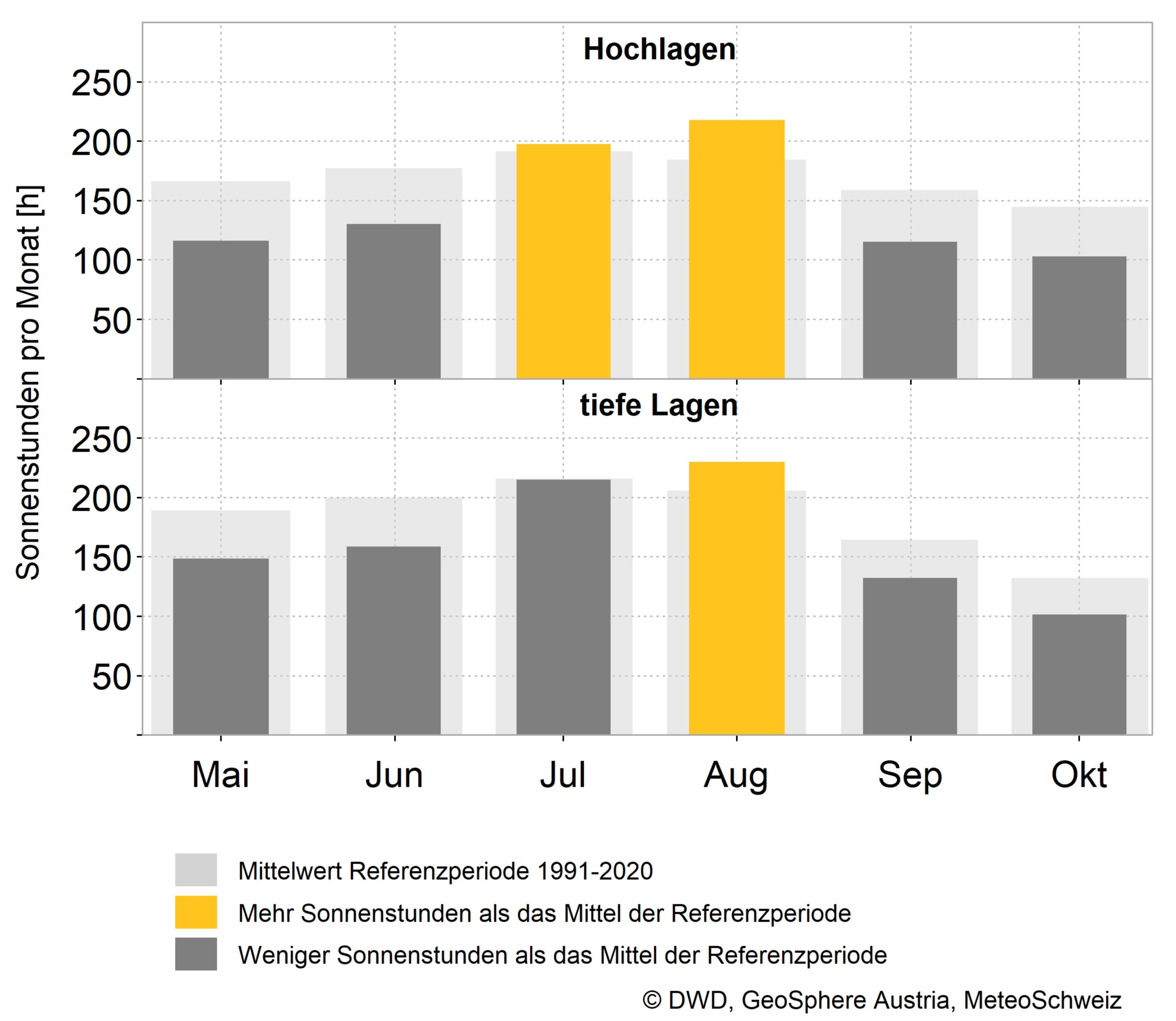
The summer half-year 2024 brought average temperatures in the Alpine region in May, June and September (comparison with the 1991-2020 climate period). July, August and October were significantly too warm, with some regional records.
For example, the warmest August of the respective measurement series in Switzerland was recorded at the Jungfraujoch, Weissfluhjoch and Säntis weather stations, as well as in Lugano and Piotta. In Austria, new August records were set in Graz, Klagenfurt, Lienz, Patscherkofel, Rauris, Sonnblick and Villacher Alpe, for example. In Germany, it was the warmest August in recorded history on the Zugspitze.
At some of the weather stations, such as Weissfluhjoch, Säntis, Zugspitze and Sonnblick, it was not only an August record, but also the warmest month on record.
In the Alpine regions of Germany, Austria and Switzerland at altitudes of 500 to 1000 metres, August 2024 usually brought 10 to 15 summer days (days with at least 25 °C). This is 50 to 80 per cent more than in an average August in the 1991–2020 climate period.
There were relatively few days of frost (below 0 °C) in the 2024 summer half-year, especially in June, July and August. In addition, from 5 July to 8 September 2024, Zugspitze (D, 2961 metres above sea level) and Sonnblick (A, 3109 metres above sea level) recorded the longest frost-free phase since the start of the respective measurement series with 66 days in a row (Sonnblick since 1886, Zugspitze since 1900). This is significantly longer than the previous longest frost-free phase at these weather stations: The previous record was 31 days at Sonnblick in 1994 and 2019, and 41 days at Zugspitze in 2022.
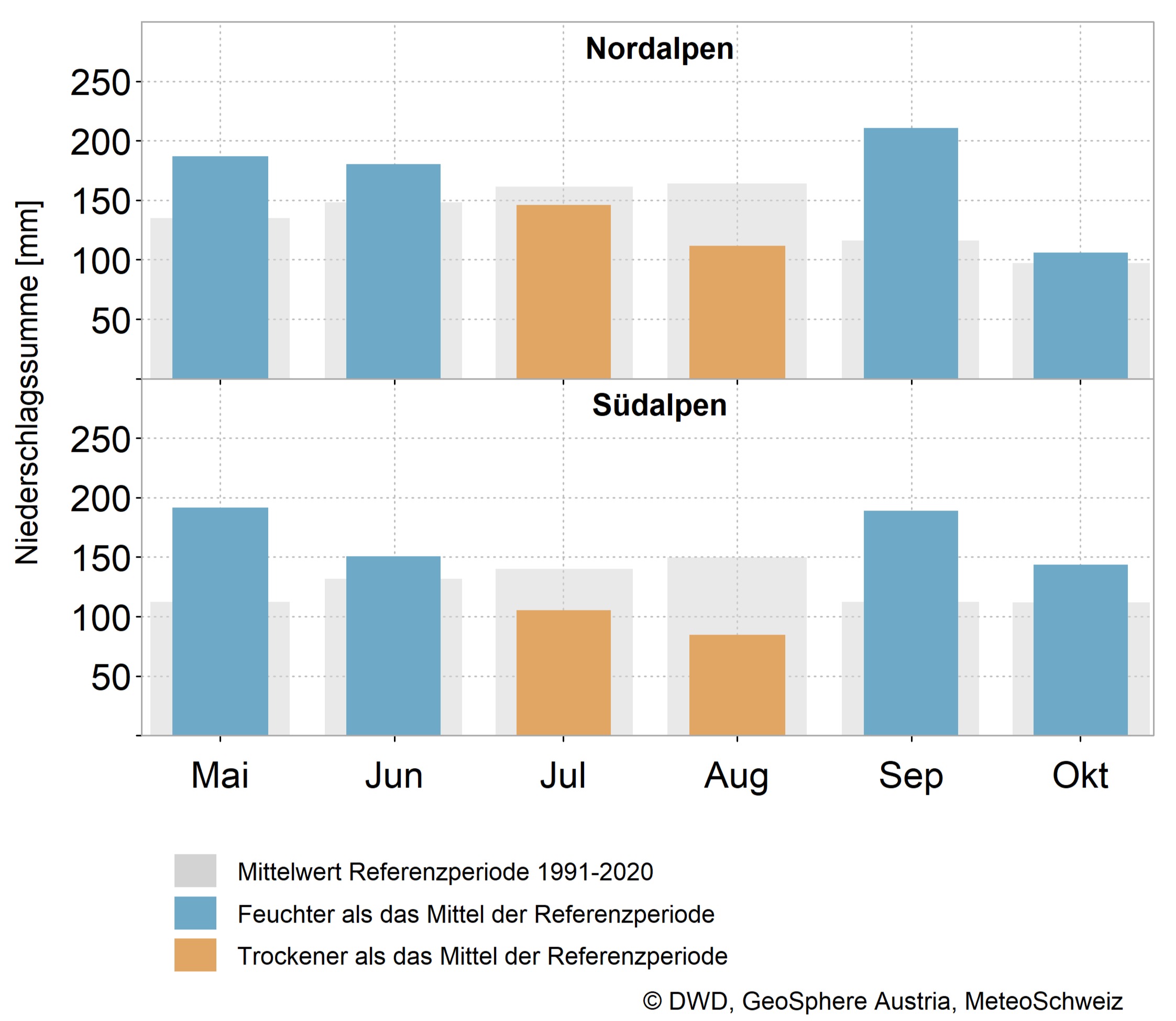
July and August 2024 were relatively dry in the Northern and Southern Alps. May, June, September and October were wetter than average and some regions experienced extreme amounts of rain.
From Switzerland to Vorarlberg to the Allgäu, there was a lot of rain, especially in May and June, which caused flooding and landslides.
For example, from 31 May to 1 June, it rained between 100 and 140 millimetres in many regions of the Allgäu. In the northern Allgäu, this corresponds to a statistical return period of 50 to 100 years. In combination with the melting snow, this led to a rise in the level of Lake Constance of around 80 centimetres within just four days at the beginning of June.
At the end of June, very large amounts of rain followed, particularly in the Swiss cantons of Ticino and Valais. On 29 June, for example, it rained 159 millimetres in one day in Binn (CH, Valais) and 101 millimetres in Simplon-Dorf (CH, Valais). In Binn, this corresponds roughly to a 10 to 20-year event. Precipitation of around 100 millimetres is exceeded in Simplon-Dorf approximately every two to five years.
In mid-September 2024, a Mediterranean low brought extremely heavy rain and flooding to the eastern half of Austria. Statistically speaking, the amount of precipitation corresponded to an event that occurs less than once every 100 years.
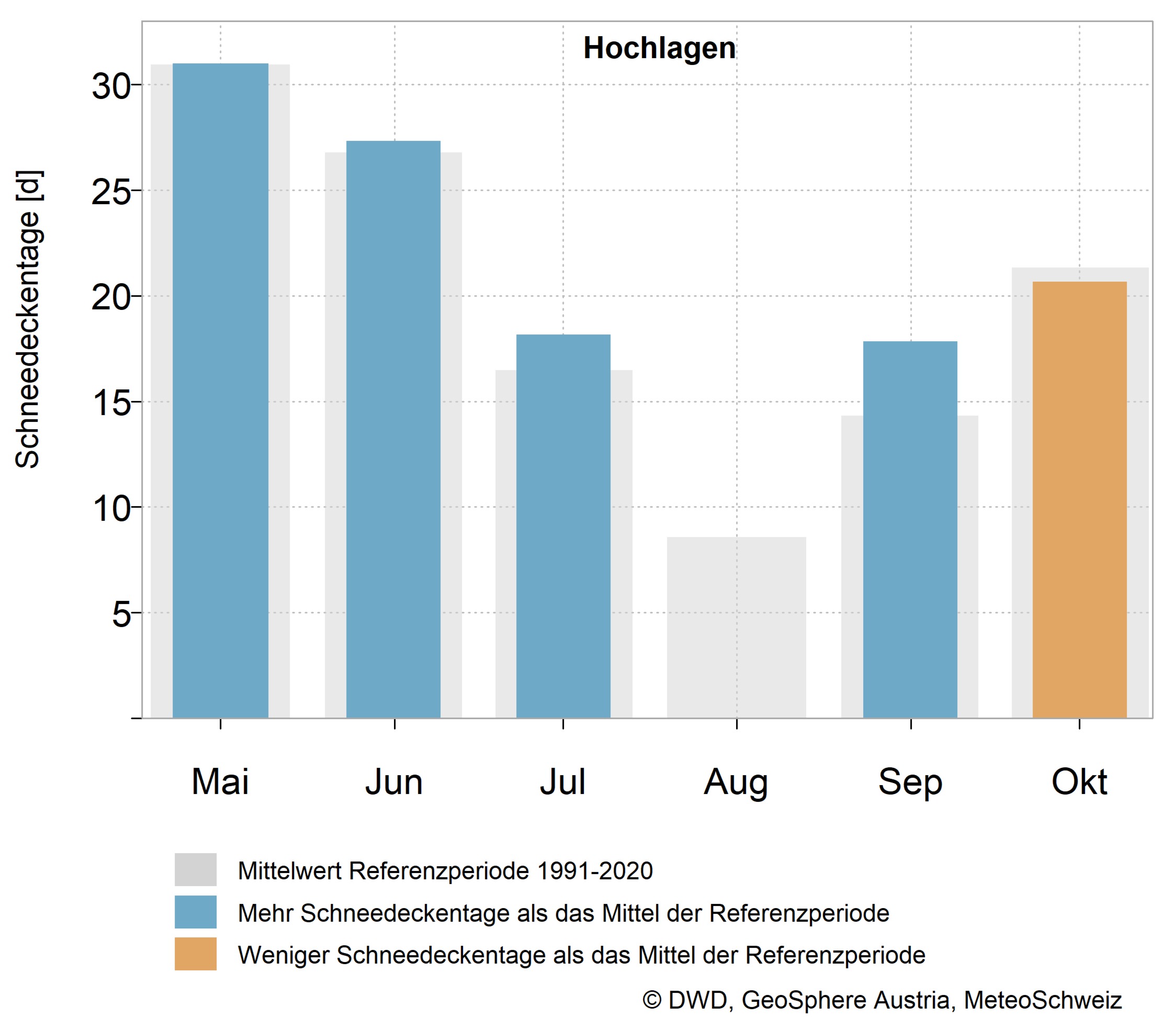
On the mountains, the large amounts of precipitation in the 2024 summer half-year resulted in an above-average number of days with snow cover in May, June, July and September.
In addition, some weather stations set a new record for snow depth in one September, for example on 15 September with 19 centimetres in Ramsau am Dachstein (A, 1207 metres above sea level) and 8 centimetres in Ruhpolding-Seehaus (D, 746 metres above sea level).
In August and October 2024, the Alps recorded less snow than average.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)